What are Epididymitis and Orchitis?
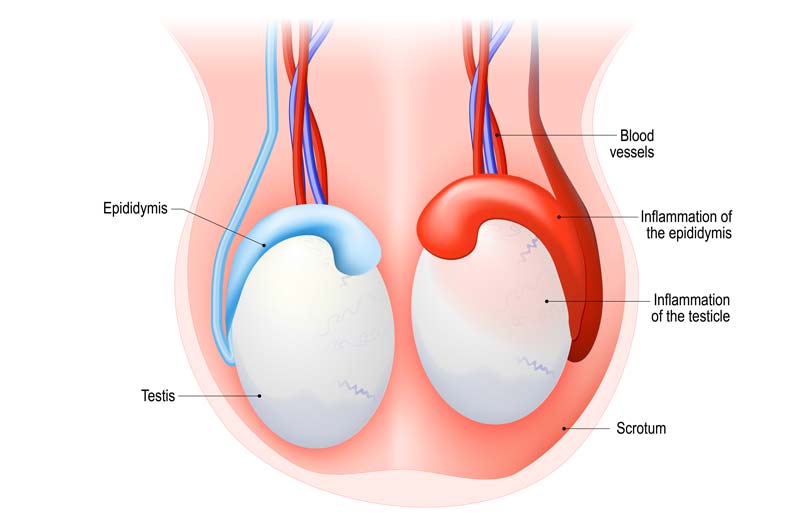
Epididymitis is inflammation of the epididymis, which is part of the male reproductive system and is responsible for the storage and transport of sperm. When this structure becomes inflamed, it can cause significant discomfort, pain, and swelling.
Orchitis is the inflammation of one or both testicles. Both conditions can happen at the same time, resulting in a condition known as epididymo-orchitis.
These conditions can cause discomfort but are generally treatable, and most patients recover fully.
What Are the Epididymis and Testes?
The male reproductive system is a complex network of structures designed to produce, store, and transport sperm.
The testes, or testicles, are the male reproductive glands. They are primarily responsible for the production of sperm and testosterone. The testes are located in the scrotum, a pouch of skin hanging outside the body, which helps maintain the optimal temperature for sperm production.
The epididymis is a long, coiled tube located at the back of each testicle. This tube is where sperm mature and are stored until ejaculation.
Epididymitis and Orchitis Symptoms
Symptoms for both epididymitis and orchitis can be similar and vary from mild to severe. The progression of symptoms might be sudden or gradual. Men who experience any of these symptoms should visit a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
- Pain and swelling in one or both testicles: These are typically the most noticeable symptoms of epididymitis and orchitis. The pain might start as a dull ache that gradually intensifies over time, or it could be a sudden, severe pain. The level of pain might also increase during physical activities or movement. Swelling in the affected testicle or epididymis might be apparent and can cause the scrotum to appear larger than usual.
- Redness and warmth in the scrotum: In response to inflammation, the body increases blood flow to the affected area. This can result in redness and a sensation of heat when touching the scrotal skin. A change in color might be visible, with the skin appearing shiny or stretched.
- A lump in the testicle: Some individuals might notice a lump or hardened area on the affected testicle. This is often a result of the inflammatory process causing localized swelling.
- Painful urination or an unusual discharge from the penis: In some cases, mainly when the inflammation is due to a bacterial infection, symptoms might extend to the urinary tract. This can result in a burning sensation during urination, the need to urinate more frequently, or a change in the color and smell of the urine. An unusual discharge from the penis might also be present, particularly in the case of sexually transmitted infections.
- Blood in the semen: This symptom, known as hematospermia, might be seen in some cases of epididymitis and orchitis. While it can be alarming, it’s usually not serious. However, it should be evaluated right away.
- Fever: A fever is a sign of an ongoing infection or inflammatory process in the body. It might be accompanied by other symptoms such as chills, fatigue, or muscle aches.
In some cases, men with epididymitis or orchitis might also experience discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse or ejaculation. Lower abdominal or pelvic pain might also be present.
Causes of Epididymitis and Orchitis
There are a variety of causes of epididymitis and orchitis. Epididymitis and orchitis can be acute, happening suddenly, or chronic, lasting for a long time. The causes can be different in acute and chronic cases.
Acute Epididymitis
Bacterial infections commonly cause acute epididymitis. Two primary culprits are gonorrhea and chlamydia, which are sexually transmitted infections (STIs). However, other bacteria can also cause epididymitis, particularly in older men and those with urinary tract abnormalities, a history of recent surgery, or catheterization.
Chronic Epididymitis
Chronic epididymitis is a long-term inflammation in the epididymis. The cause of chronic epididymitis isn’t always clear, but it’s often associated with long-standing infections, urinary tract abnormalities, or prostate problems.
Orchitis
Orchitis can result from a bacterial infection, including sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea or chlamydia. Viral infections, like mumps, can also lead to orchitis. In many cases, the cause of orchitis is challenging to identify.
Acute Epididymo-orchitis
This condition is an inflammation of both the epididymis and the testicle. It’s often caused by the spread of bacterial infection, particularly STIs, in young, sexually active men.
Diagnosis
There are multiple steps in diagnosing epididymitis and orchitis. The first step is a detailed discussion of symptoms, their duration and severity, and any potential exposure to risk factors, such as sexually transmitted infections or urinary tract abnormalities.
Then, the physician will perform a physical examination. Testicles and the area of the epididymis will be examined to look for signs of swelling, redness, and tenderness. The doctor may feel for enlarged lymph nodes in the groin. The penis may be inspected to identify abnormal discharge.
Laboratory Tests
Determining if epididymitis or orchitis is present and what may be causing the condition often includes several laboratory tests, including:
- Urinalysis and urine culture: Urinalysis involves testing a urine sample for signs of infection, such as the presence of white blood cells or bacteria. A urine culture may also be performed to identify the specific type of bacteria causing the infection.
- Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs): These tests identify sexually transmitted infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia. A sample for NAATs can be collected through a urine sample or a swab inside the penis.
- Blood tests: In some instances, blood tests might be needed to check for signs of infection elsewhere in the body or to exclude other potential causes of symptoms.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, like those listed below, provide a detailed view of the scrotum and its structures.
- Scrotal ultrasound: This painless test uses sound waves to produce images of the structures within the scrotum. It helps determine whether there is inflammation in the epididymis or testicle. It can also exclude other conditions, such as testicular torsion.
- Nuclear scan of the testicles: This test involves injecting a small amount of radioactive material into the body. This material travels through blood vessels and can highlight areas of inflammation. Though not commonly used, it may be beneficial in some instances.
Treatment for Epididymitis and Orchitis
Treatment strategies for epididymitis and orchitis aim to alleviate symptoms, eradicate the infection, and prevent potential complications. The exact treatment plan may differ based on several factors, including the cause of the condition and the severity of symptoms. Common treatment options include:
- Antibiotics: If a bacterial infection is the underlying cause of epididymitis or orchitis, antibiotics will be prescribed. The specific antibiotic depends on the bacterial species identified as the cause of the condition. It is imperative to complete the entire course of prescribed antibiotics to prevent the infection from returning, even if symptoms improve.
- Pain management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, are often recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In cases of severe pain, stronger pain relief medication may be prescribed.
- Rest and support: Adequate rest, particularly with an elevated scrotum, can reduce discomfort and speed recovery. This can be achieved by lying down with a folded towel under the scrotum. An athletic supporter can provide additional support.
- Follow-up testing: Upon completion of treatment, repeat testing may be advised to ensure the infection has been completely resolved. This is particularly important if the condition is due to a sexually transmitted disease.
- Hospitalization: In rare cases, hospitalization may be necessary if the infection is severe or complications arise. Complications could result from the formation of an abscess (a pocket of pus) or if the infection spreads to other parts of the body.
- Surgery: Although rarely required in cases of epididymitis and orchitis, surgical intervention may be needed if complications such as an abscess or severe damage to the epididymis or testicle occur.
Treatment is primarily symptomatic for viral orchitis, like that caused by mumps. In these cases, treatment involves the use of over-the-counter pain relievers, rest, and scrotal support while the body combats the viral infection.
It is important to note that while these treatments can relieve symptoms and address the underlying cause, they cannot reverse any damage already inflicted on the epididymis or testicles due to the inflammation. Therefore, it’s important to see a doctor immediately when symptoms arise.
Complications
If left untreated, epididymitis and orchitis can lead to serious complications. These can include abscess formation, chronic pain, and, rarely, reduced fertility. Therefore, early diagnosis and
prompt treatment are essential.
Prevention
Prevention of epididymitis and orchitis mainly revolves around safe sexual practices and good hygiene. Condom use during sexual activity can prevent STIs, a common cause of epididymitis and orchitis. The mumps vaccination can also help prevent mumps orchitis. Regular check-ups can detect any potential issues early.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can epididymitis and orchitis affect fertility?
These conditions can sometimes affect fertility, especially if they are not treated. However, with proper treatment, the impact on fertility is generally minimal.
Can these conditions be prevented?
While preventing all cases of epididymitis and orchitis may not be possible, safe sex practices and regular check-ups can reduce the risk.
Is treatment for epididymitis and orchitis always necessary?
Yes, treatment is essential not only to alleviate symptoms but also to prevent complications.

